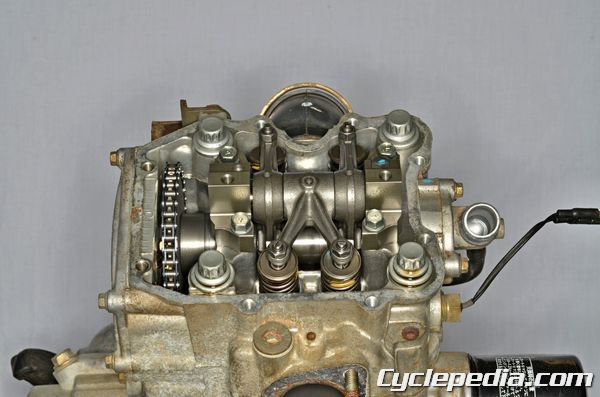
Many of the engines that power Polaris ATV’s are liquid cooled, single cylinder, SOHC 4-stroke units manufactured by Fuji. The 400, 450, and 500 cc engines are nearly identical outside of bore and stroke. The newer 550 engine is updated, but some of these tips still apply. The 570 engine has a DOHC head and unrelated for the purpose of this article.
The popularity and sheer production numbers of these ATVs leads to a high demand for service and repair for their Fuji engines. There are a few important tips to keep in mind when servicing one of these engines. This article will give some service specifications and procedures that apply to many of these power-plants, but it is important to have the service manual for the particular vehicle to ensure any minor differences are noted and specific procedures are followed as required by the OEM.

To start with, metric tools will be required. Specifically a set of high quality 12-point sockets will be needed if the cylinder head and cylinder must be removed. The large cylinder head bolts require a 14 mm 12-point socket, and the cylinder bolts require a 12 mm 12-point socket.

The engine should be set to TDC on the compression stroke when checking the valve clearance or removing or installing the rocker arms and camshaft. Unlike many engines, there isn’t a quick access plug to be able to rotate the crankshaft by hand with a wrench or socket. Position the crankshaft at TDC on the compression stroke by gradually rotating the crankshaft with the recoil starter. Observe the position of the flywheel through the timing inspection hole and the camshaft sprocket position. The camshaft sprocket locating pin should be pointing up, away from the cylinder, and perpendicular to the cylinder head mating surface at the same time the flywheel TDC mark is lined up with the timing inspection hole.

Remove the camshaft opposite side of the engine from the camshaft sprocket. Inspect the camshaft, cylinder head and rocker arms for damage, and compare the component measurements and clearances to the factory specifications. Inspect the function of the automatic compression release system. Make sure the weight and return spring for the automatic compression release system are installed correctly when the engine is assembled. Inspect the valve clearance after the camshaft and rocker arms are installed.

Loosen the cylinder head and cylinder bolts a 1/4 turn at a time in a crisscross pattern. On assembly, apply fresh engine oil to the washers, threads and flanges of each large cylinder head bolt. Install the large cylinder head bolts and thread them in by hand. The cylinder head bolts require a multi-step tightening sequence. Tighten the large cylinder head bolts evenly, in a crisscross pattern, according to the stages below with a high quality 12-point 14 mm socket. Place a mark on the head of the cylinder head bolts to aid in the degree loosening and tightening steps.
| Cylinder Head Bolt Torque | |
|---|---|
| Cylinder Head Bolts Torque (Step 1) | Tighten 22 ft-lb |
| Cylinder Head Bolts Torque (Step 2) | Tighten 51 ft-lb |
| Cylinder Head Bolts Torque (Step 3) | Loosen 180 degrees (1/2 turn) |
| Cylinder Head Bolts Torque (Step 4) | Loosen 180 degrees (1/2 turn) |
| Cylinder Head Bolts Torque (Step 5) | Tighten 11 ft-lb |
| Cylinder Head Bolts Torque (Step 6) | Tighten 90 degrees (1/4 turn) |
| Cylinder Head Bolts Torque (Step 7) | Tighten 90 degrees (1/4 turn) |

The crankshaft, balancer shaft, and oil pump all have shims that are installed inside the crankcase to set the end play. Measure the bearing depth with a straight edge and the width of the component and old shim with calipers. Subtract the component width and old shim thickness from the total distance between the crankcase bearings. This end play clearance should be 0.008 – 0.016 in (0.2 – 0.4 mm). Replace the shim as needed for each component so the end play is in specification.

The Cyclepedia Online Service Manual for the Polaris Sportsman 400, 450, and 500 models is currently in production and will be available soon. This full color online manual will cover all service procedures from wheel hub bearing replacement to transmission shaft assembly.


Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.